
Standardizing Guyanese Phone Numbers
Proper phone number formatting using E.123 and E.164 standards ensures clarity, reduces miscommunication, and enhances international dialing accuracy, particularly for Guyanese numbers. This guide addresses common mistakes and best practices.
- What is a Standard Phone Number?
- Importance of a Representing Phone Numbers in a Standard Format
- Phone Number Standards
- How Standards Impact our Communications?
- Common Mistakes While Writing Phone Numbers
- Conclusion
What is a Standard Phone Number?
When you intend to call someone on their cellular mobile phone, the first thing that comes to mind is the intended person's phone number. Of course, it is the established way to differentiate and identify one person's phone number from another, but there is more to it. How is it correctly written? How should it be told to persons who want to communicate with you from outside of Guyana?
The answer to all of that is "standards". Humans are divided by many factors, but we work seamlessly together through standards. In this brief article, we will explore the standards of phone number, the notation and structure, particularly as it relates to Guyana. We will appreciate how standards are important and also explore the common mistakes when dealing with phone numbers and the potential problems these mistakes embody. Finally, we will detail ways to avoid such mistakes.
Importance of a Representing Phone Numbers in a Standard Format
A phone number is a piece of identity that a person owns, through which that person may be communicated. Simple mistake in dialling the number may lead to a completely different person than intended. Further, mobile numbers are tied up to the identity of an individual, so much so that it may be used to authenticate and authorize in crucial areas such as banking and security. As such, it is firstly important to ensure once you receive your phone number, you secure it and do not allow unauthorized access. Secondly, you and those who intend to reach you through the phone number, dial the phone number correctly, in a standard format.
Phone Number Standards
Let us take a look at how a phone number should be officially used/represented. Subsequently, we will also follow the trails that lead to international bodies that are responsible for articulating the standards of phone numbers.
In the Guyana, it is very common to represent the phone number of a person by simply use the 7 digits provided by the phone carriers (GTT (Guyana Telephone and Telegraph), Digicel and ENET (Everything Network)), example: 7123456. This format of writing phone numbers is acceptable, but not the correct way (for good reasons). Imagine if the number was: 7222224. It's already a strain on the eyes to count how many 2s are in that number. Or even worse, 7233223. Now things are getting not only straining on the eyes, but confusing in the brain.

The simple solution to it is to segment the 7-digit number to smaller more easily readable sections. For example, add a space between the first 3 digits and the last 4 ones, like, 723 3223. This may sound obvious, but there is actually a standard backing this, called E.123.
E.123 Standards
E.123 is a standard developed by the International Telecommunication Union - Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T), that defines the notation for national and international telephone numbers, e-mail addresses and web addresses. The ITU is actually one of the oldest international bodies that predate United Nations (UN), and became a part of it after its formation. Though countries are not legally bound to follow these standards and practices, but if they do not do so, they may experience confinement and seclusion in the telecommunication sector. According to the E.123 standard notation for telephone numbers, only spaces (or unless agreed upon explicit symbol like hyphen) should be used to separate the digits.

E.123 is to describe the notation of the phone numbers in writing. However, since our modern mobile phones are advanced enough, while entering the numbers for calling/saving, it automatically places the relevant separator/spaces where necessary according to this standard. When dealing with international numbers, or Guyanese numbers but from networks and carriers outside Guyana, there are a few crucial considerations.
E.164 Standards
Though E.123 focuses on the notation and presentation of the phone numbers, there is another standard, E.164, that deals with the structure and format of the phone numbers. E.164 defines what segment of the phone number should come in what order. Example, according to E.164, the format should be as follows:
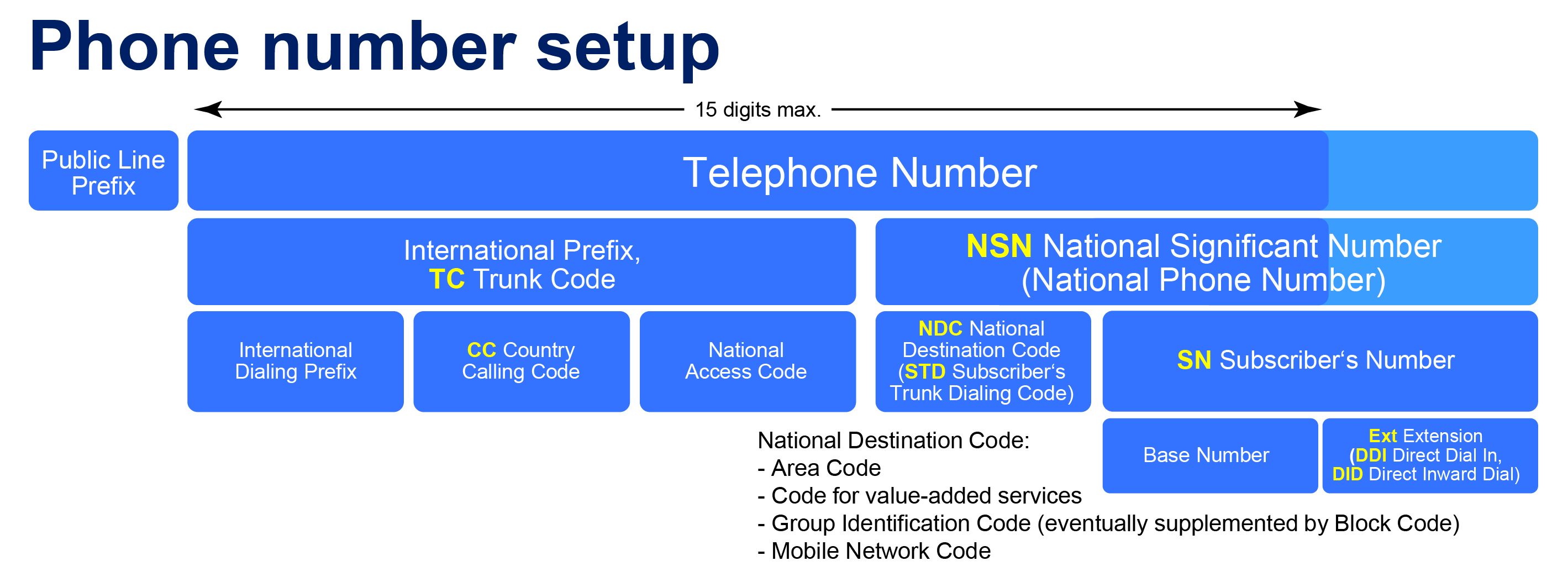
Let's analyse the image above and see how it implies to Guyanese phone numbers:
- Public Line Prefix: Not included in international formats. Usually used in countries that require a prefix to be entered before dialling a public phone number.
- Telephone Number
- International Prefix, TC - Trunk Code
- International Dialling Prefix: '+' symbol used to start international numbers.
- CC Country Calling Code: The country code for international numbers, example: 592 for Guyana
- National Access Code: Typically used in some countries for domestic calls, not applicable in Guyana.
- NSN National Significant Number (National Phone Number)
- NDC National Destination Code (STD Subscriber's Trunk Dialling Code): Represents an area or service within the country, for example, 222 for a GTT Landline in Georgetown, 710 for ENET Cellular.
-
SN Subscriber's Number
- Base Number: The specific local number assigned to the user (the last 4 digits), for example, 1234 in +592 711 1234.
-
Ext Extension (DDI Direct Dial In, DID Direct Inward Dial): Internal extensions of the phone number, typical in institutional, organizational or business phone numbers. Not widely used in Guyana. Example: x5678.
Note: though the E.164 standard defines where the Extension number comes in the structure (at the end), the extension is not part of the E.164 standard number format.
- International Prefix, TC - Trunk Code
The watered down example of the above would be: +592 226 1234.

Tip: If you have multiple numbers of the same entity with the same NDC (example: 226), then according to E.123 standards, the 4 digits may be noted after a slash (/) separator, for example, +592 222 3456 / 7890.
How Standards Impact our Communications?
For a small country like Guyana with a comparably small population, phone numbers are simple 7 digits and fortunately are free from complexities. Nonetheless, this should not be taken for granted, because misrepresentations still impact our daily communications.
For example, when phone numbers are saved in your phone in the local format (like, 609 8765), when trying to dial the number from abroad (outside Guyana), especially with a non-Guyanese carrier, you may face errors (depending on the carrier, country and the application you use to save the phone numbers). So a basic rule of thumb for Guyanese numbers is to always save them and/or represent them in documentations, in their complete international format, like +592 609 8765. This way, it does not matter weather you dial it from within Guyana or outside, you are certain that you have followed the standards and are more than likely to ring the person you intend.
Note: not all countries strictly follow the implementation of the E.164 standard. This means that in certain countries like Argentina, even if you have saved the number in the E.164 international format, you may have to apply a few changes before dialling the intended number. Nonetheless, in the majority of the countries and carriers, E.164 standards are strictly applied.
Finally, it is crucial that in official documentations (both online and printed), the international E.123 and E.164 standards are adhered to in notation and structure. Unfortunately, many official letters, websites and other documentations have embarrassing notation/structure. We will look at a few of them below.
Common Mistakes While Writing Phone Numbers
- +1 (592) 222 3456: This number will dial a phone number 222 3456 in Rocky Springs, Wyoming (592 is the area code) in the United States of America (+1 is US country code). More about why some people make this mistake below.
- (592) 222 3456: Though when dialling in Guyana, carriers may be forgiving and either drop your call or apply corrections before routing your call to the intended person's device, but this is definitely bad notation. 592 is the area code (since surrounded in parentheses) and such numbers can easily be mistaken with the local 10-digit phone numbers of countries like US and Canada.
- 5922223456: Again you might locally be able to get through to the intended persons, but this structure/notation is misleading to the international audience as many persons globally are not aware or do not assume subconsciously that 592 is the country code and may assume that it is the phone number to which country code (an additional +592) is to be added.
Note: +592 222-3456 or +592-222-3456 are completely valid notations of Guyanese numbers and will reach the intended person. Though we still do recommend adhering to one of either of the following representations for better consistency:
+592 222 3456 or +592 222-3456

North American Numbering Plan (NANP) and Its Influence in the Caribbean
Caribbean countries like Jamaica (+1 (876) XXX XXXX), Trinidad and Tobago (+1 (868) XXX XXXX), Barbados (+1 (246) XXX XXXX) and Saint Kitts and Nevis (+1 (869) XXX XXXX) are a part of NANP which shares the +1 international country code but have different area codes (as shown in the parenthesis). Practically, the local numbers are 7 digits just like Guyana, but their standard international notation differs from that of Guyana, since Guyana proudly follows its own independent numbering plan (with the international code +592).
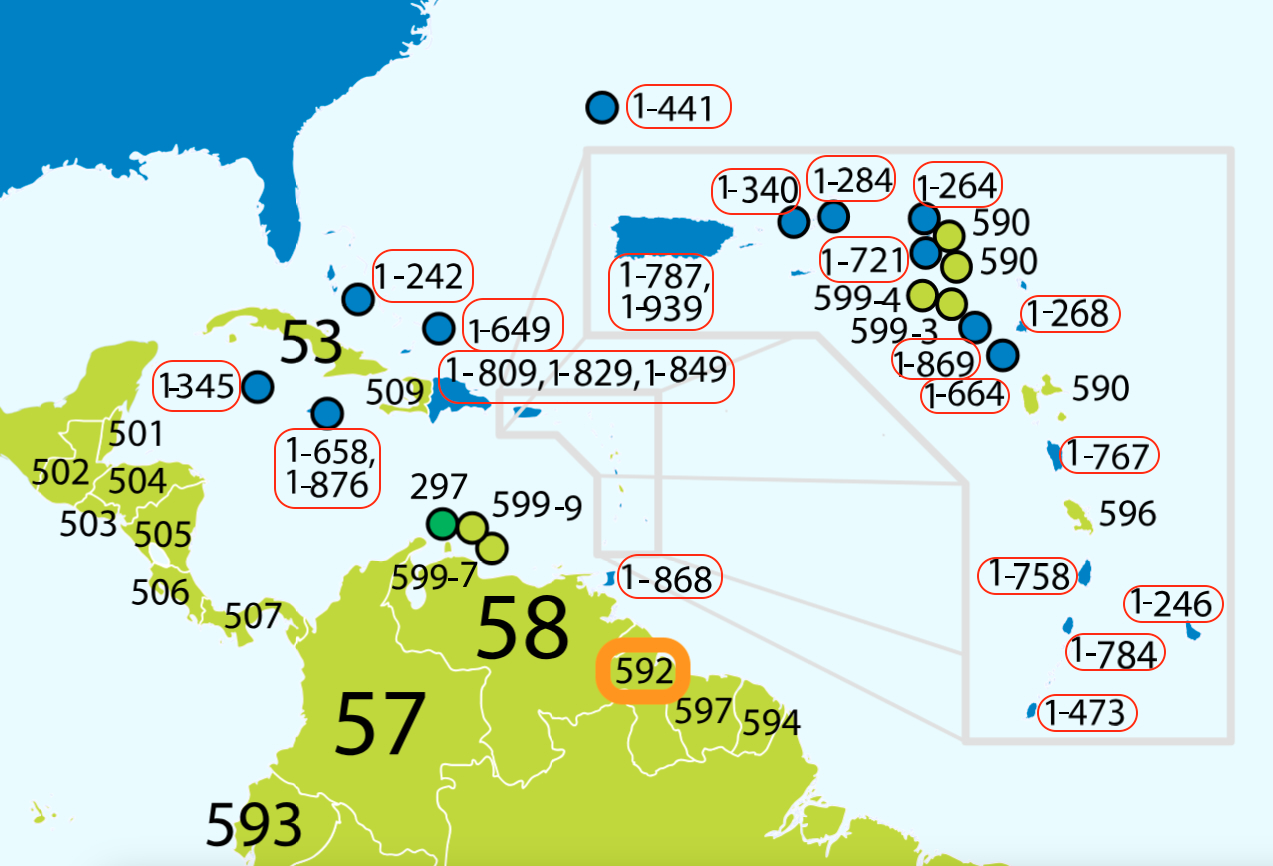
This is why when businesses from other CARICOM countries are established in Guyana, more often than not, you are likely to see the +1 international code before 592, because they are familiar with it and assume Guyana being a part of the Caribbean, is also a part of NANP. This form of notation is a mistake and will lead to errors and inconsistencies in the documentations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, adhering to phone number standards like E.123 and E.164 is essential for effective communication and avoiding errors, especially in a global context. While Guyana has a simple 7-digit local format, representing numbers in the correct international format ensures consistency and reduces miscommunication. By following these standards, you can avoid common mistakes and ensure your phone numbers are correctly interpreted, whether for local use or international dialling. This is crucial not just for personal communication, but also for official documentation.